




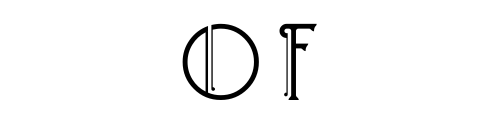



























Sector Disruption. Syndicate Efficiency. On-Oath Results.
Native Chaos Holdings LLC is a Native American owned and managed company that advocates for Native American rights, cultural reform, and economic prosperity. The company operates for-profit ventures and manages partnerships within its syndicate, each focusing on our Tribal and Native American growth sectors.
We Handle It So You Don't Have To.
We are available at any time
Chaos News.
Everything about chaos.














